News updates written by CIWM’s commercial partners.
| Greyparrot | Greyparrot gathers global waste leaders to help MRF operators plan for a profitable 2026 |
| Beyondly | Case Study: Empowering Tradelinens on their B Corp Journey |
| Probe Industries | Probe Industries launches market-first odour enhancement technology to help industrial facilities reduce odour complaints and improve on-site wellbeing |
| CONTENUR | CONTENUR supports the transformation of Inverness Castle with discreet underground waste solutions |
| Rubbermaid Commercial Products | Rubbermaid Commercial Products launches new range of stylish yet functional solutions for small spaces |
| CRJ Services | Specialist NPORS Training for Waste, Recycling & Forestry Machinery |
| Vision Techniques | Vision Techniques revamp best-selling product reflecting the changing needs of modern fleets |
| Dennis Eagle | Dennis Eagle and Terberg Matec UK’s Sales and Aftermarket teams have integrated |
Greyparrot | Greyparrot gathers global waste leaders to help MRF operators plan for a profitable 2026
As margins continue to tighten, the UK’s material recovery facilities (MRFs) are under pressure to do more with the material and machinery they already have.
Faced with rising gate fees, the approach of DRS and Simpler Recycling, and fluctuating commodity prices, AI automation has emerged as a survival tool. Before deploying waste intelligence systems, many operators still need to distinguish AI hype from use-cases that actually increase margins.
An upcoming Greyparrot webinar brings together global facility operators and technical experts to focus on practical changes and proven impact. Leaders that already use waste intelligence technology will share what AI has changed, what remains the same, and how the technology factors into their strategies for 2026.
Running a profitable MRF in 2026: What AI really changes – and what it doesn’t takes place on Thursday 12 February 2026 at 14:00 GMT, and registration is now open.
How facility operators actually use AI
Instead of focusing on future promise, the discussion will centre on real-world experience from organisations that have already embedded AI waste analytics in their operations. Greyparrot says it chose its panel to provide global context for the challenges facing British recyclers.
Speakers include experts from KSI Recycling, GreenTech and USA Waste & Recycling. While each applies AI to different regulatory contexts, waste streams and commercial targets, all share a focus on profitability and efficiency.
The session will be hosted by Greyparrot’s Matthew Steventon, who is embedded in the UK’s waste sector and has helped facilities across the country to determine practical use-cases for AI waste analytics. Steventon will draw out the tangible value that AI has delivered for each operator, and find out where human expertise is irreplaceable.
Revealing the strategy behind the headlines
Waste intelligence technology made headlines for increasing both recovery rates and revenue in 2025. Speakers will share the specific actions they took with the help of Greyparrot’s Analyzer system, and how they plan to achieve more newsworthy results in 2026.
As GreenTech’s CTO, the UK’s Alan Smith helms the company’s multinational AI strategy that has already resulted in 10% more PET recovery revenue. He will share how his team accounts for variations in regional infrastructure and regulation, offering a rare look at how one of Europe’s largest PET recyclers uses AI in 2026.
KSI Recycling’s Plant Manager Foppe-Jan de Meer will reveal how his team used AI insights to boost recovery rates by 10% – mitigating avoidable losses and a growing compliance risk. For UK recyclers looking to prepare for DRS, de Meer offers valuable perspective from the Netherlands, where operators have been adapting to deposit returns since 2006.
USA Waste & Recycling’s Brian Popovich is financial analyst for Murphy Road Recycling. As a Senior Financial Analyst, Popovich will detail how he evaluates AI’s commercial impact at America’s “MRF of the Year”, which saw the country’s first plant-wide deployment of Analyzer units in 2025.
A realistic look at AI’s impact in 2026
By comparing experiences across regions, Greyparrot says its session will give UK attendees a clear understanding of how waste intelligence technology has helped their counterparts adapt to regulation and commodity pressures, enabling them to build that experience into their own operations for 2026.
The session will also feature a Q&A session for attendees that have specific questions about AI’s role in waste management this year.

Register on Greyparrot’s website to secure a place on 12 February: Join the webinar
Beyondly | Case Study: Empowering Tradelinens on their B Corp Journey

Background
Tradelinens are an importer and wholesaler of luxury textiles, supplying premium products predominantly to the hospitality industry, but also direct to consumer via ecommerce.
Tradelinens strongly believe the textiles industry plays a crucial role in shaping a more sustainable future, and have a long-standing commitment to ethical trading, sustainable sourcing, and placing people at the heart of what they do.
Back in 2016, Tradelinens were the first UK trade linen supplier to join the Better Cotton Initiative (BCI), just one of the steps they have taken to reduce environmental impact and help people and communities thrive. This commitment has allowed Tradelinens to financially support the improvement of farmers’ livelihoods, sustainable cotton growing, and the empowerment of women within cotton farming. In 2024, they also proudly achieved their Global Organic Textile Standard (GOTS) certification, a worldwide leading textile processing standard.
The Opportunity
In 2024, Tradelinens approached Beyondly, a fellow B Corp, for expert guidance and support as they progressed on their own journey towards becoming a certified B Corporation.
Tradelinens were also receiving external stakeholder pressure to measure their carbon impact, an element they would be scored on as part of B Corp’s rigorous B Impact Assessment as well. Faced with a complex supply chain and internal structure, where clarity over the scope and boundary of carbon footprint measurement was unclear, Beyondly helped Tradelinens navigate this complexity with a carbon management solution that aligned both with the requirements of their stakeholders and B Corp assessment.
The Solution
The Beyondly team delivered a tailored sustainability solution for Tradelinens that aligned with their goals, values, and external requirements; including carbon management support, conducting a materiality assessment, and comprehensive B Corp consultancy.
Beyondly worked closely with Tradelinens to set the boundary of their UK carbon footprint and conduct full Scope 1 and Scope 2 emission calculations for both 2023 and 2024. In depth analysis on energy data was conducted, to identify key emission hotspots and areas of highest impact. All findings were presented in a report, which also detailed assumptions and actions to support emission reductions. In addition, guidance was provided on improving calculation accuracy year on year, enabling more robust reporting going forward.
A materiality assessment was conducted, which included identifying relevant ESG factors for stakeholders to rank by importance; providing Tradelinens with insight into what matters most to their employees, shareholders, customers, suppliers, and partners, to ensure their goals aligned with this. Alongside analysis of the results and a materiality matrix, Beyondly provided Tradelinens with the practical next steps they could take to drive their impact further and achieve long-term sustainability.
Becoming a B Corp is a commitment to balancing people and planet alongside profit, requiring businesses to successfully pass a rigorous and complex assessment. Beyondly discussed the B Corp certification formalities and process with Tradelinens, to ensure confidence and clarity on each step of their journey.
Upon gaining an in depth understanding of Tradelinen’s business activities, processes, and current environmental and social standards, Beyondly carried out a detailed review of their B Impact Assessment responses to highlight areas for improvement and provide suggestions on what evidence to collate. The provision of a RAG (Red, Amber, Green) report laid out an action plan outlining recommended improvements, including advice regarding claimed and unclaimed points, for Tradelinens to develop and strengthen their strategy further.
The Results
Tradelinen’s carbon footprint report and the results of their materiality assessment helped provide the basis of, and content for, their first sustainability report in 2024, along with enabling them to focus their goals on what matters most to the Tradelinens community.
The calculation of their Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions spurred Tradelinens to take a further step towards helping to drive positive environmental impact. Through purchasing certified carbon offsets, Tradelinens are helping to fund projects that contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions such as tree planting, protection and restoration initiatives, and biodiversity enhancement.
Following partnering with Beyondly and the completion of their B Corp consultancy project, Tradelinens’ B Impact Assessment score increased from 59.4 to 76.8. In October 2025, they celebrated a significant milestone – successfully certifying as a B Corp with a final score of 83.4, and joining a community of companies passionate about using business as a force for good to positively impact society and the environment.
Reflecting on Tradelinens’ B Corp journey and partnership with Beyondly, Catherine Morris, Managing Director at Tradelinens, commented: “From our first contact with the team at Beyondly at the start of 2024, they have provided outstanding, practical guidance throughout two years of Scope 1 and 2 measurements and our successful B Corp certification. As a small team, we particularly valued their expert advice, clear communication, and user-friendly templates.”
While we have been focused on strengthening our ESG journey since joining BCI in 2016, it can be challenging for SMEs to manage such specialist work internally. Beyondly integrated seamlessly with our team, and I would highly recommend them to any company, whether you’re just beginning your ESG journey or looking to add greater structure and rigour to existing plans.”
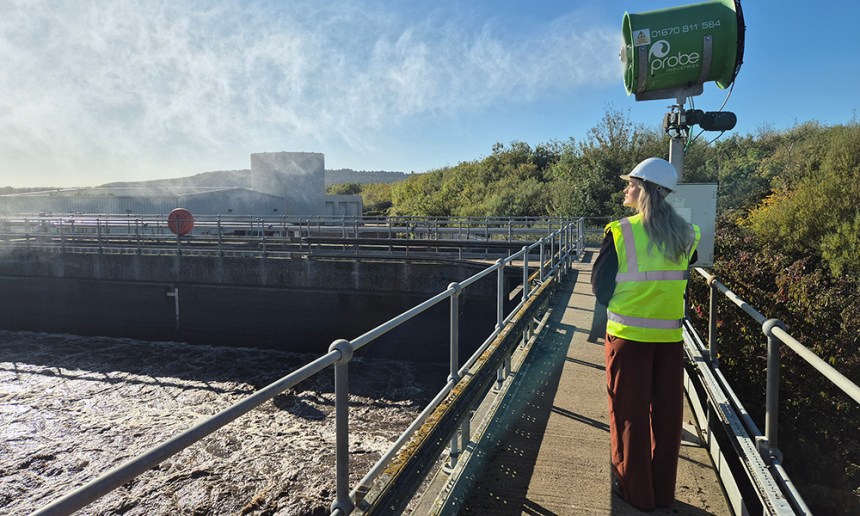
Probe Industries | Probe Industries launches market-first odour enhancement technology to help industrial facilities reduce odour complaints and improve on-site wellbeing
Probe Industries, a global innovator in industrial odour and dust control technology, has launched an industry-first odour enhancement solution that transforms air quality at industrial sites to meet legal requirements for cleaner, healthier and more sustainable environments for workers, visitors and surrounding communities.
Industrial environments – including waste management, water treatment and processing facilities – are often associated with persistent, unpleasant odours that can affect workers and people living in surrounding areas. Evidence links poor air quality and malodours with headaches, irritation, tiredness, low mood, stress and other health-related symptoms, with waste and recycling sectors recording significantly higher sickness absence (12.3 days compared to 6.4 days) than typical UK averages according to the Health and Safety Executive.
At the same time, operators face increasing pressure from regulators and local communities to improve air quality and control odour and emissions in line with environmental laws and permit conditions.
Based on Probe Industries’ leading AiroPure® odour neutralisation technology used widely across the waste management, water treatment, healthcare and hospitality sectors, new AiroVive®, is the world’s first industrial odour enhancer that combines a biodegradable, non-toxic odour neutraliser with mood-boosting fragrance design.
AiroPure is a patented odour elimination solution which works at molecular level to destroy odours and harmful compounds at industrial manufacturing, processing and treatment plants. Independent performance tests show a 100 percent reduction in sulphur dioxide and hydrogen sulphide emissions and a 99.4 percent reduction in ammonia and amines, with employees at trial sites reporting a significant improvement in air quality and working conditions.
With AiroPure’s proven odour neutralisation technology at its core, AiroVive not only captures and contains odour at source but also adds a bespoke, mood-enhancing fragrance to boost wellbeing. The innovative formula is non-hazardous, non-toxic and ISO 14001 compliant to meet environmental responsibility targets.
The odour enhancement technology can integrate directly into existing misting, direct spray and liquid injection operations for flexible deployment across a wide range of applications, including transfer stations, landfill sites, recycling facilities and water processing operations.
Victoria Taylor, CEO at Probe Industries comments, “Industrial odours affect local air quality as well as workplace performance and productivity. We have worked with world-renowned fragrance experts to design a diverse range of scents inspired by the restorative powers of nature and tailored to accompany our proven underlying odour control technology.”
“Based on more than 30 years of neuroscience and developed using detailed consumer research supported by artificial intelligence, AiroVive replaces unpleasant odours with mood-enhancing fragrances, showing a strong commitment to both the workforce and the local community, and demonstrating full regulatory compliance.”
AiroVive is the latest extension of Probe Industries’ world-class portfolio of patented systems which help make industrial environments cleaner, safer and more sustainable in compliance with ISO 14001. Market leading solutions include AiroNaut , ProFog
, ProFog , ProActive
, ProActive , ProDry
, ProDry and ProRain
and ProRain , which offer targeted odour removal, dust suppression and misting applications.
, which offer targeted odour removal, dust suppression and misting applications.
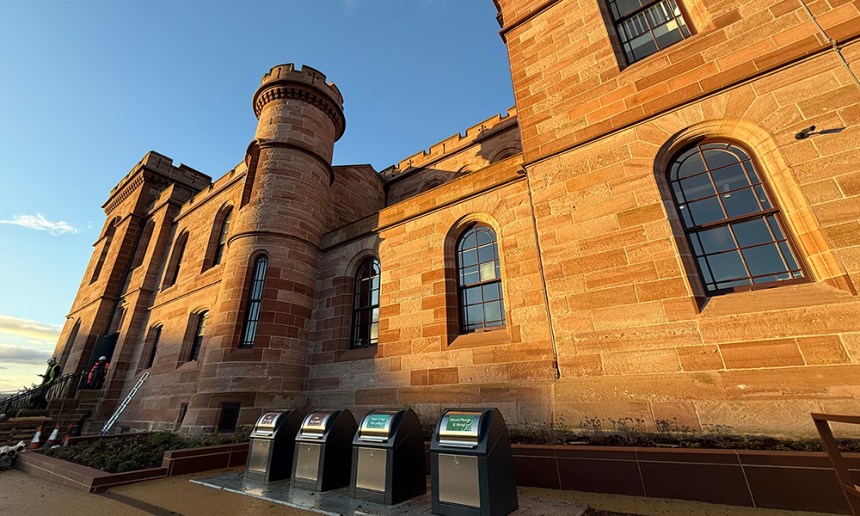
CONTENUR | CONTENUR supports the transformation of Inverness Castle with discreet underground waste solutions
CONTENUR has played a key role in the £47 million transformation of Inverness Castle, supplying a modern underground waste management solution for one of Scotland’s most significant heritage redevelopments, which officially reopened to the public in December.
Now operating as a world-class visitor attraction and cultural gateway to the Highlands, the reimagined Inverness Castle features rooftop viewing platforms, landscaped terraces, café spaces and fully restored historic interiors. The redevelopment has been carefully delivered to enhance the visitor experience while preserving the castle’s commanding presence above the River Ness.
With visitor numbers significantly increased since reopening, effective waste management was a critical consideration from the outset. Traditional above-ground containers were deemed unsuitable for such a sensitive and historically important site, as visible infrastructure would have disrupted key sightlines and detracted from the castle’s iconic character.
To address this challenge, CONTENUR was selected to deliver a Hydraulic Underground Container System that combines operational efficiency with minimal visual impact. Installed below ground level, the system enables waste to be managed safely and hygienically while remaining virtually invisible within the surrounding landscape.
The project specified CONTENUR’s Evolution model disposal columns, selected for their clean, contemporary design and proven durability in high-footfall public environments. The system was carefully integrated into the redevelopment layout, aligning with new terraces and pedestrian routes to ensure ease of use for visitors and practicality for day-to-day operations.
Working in close collaboration with Bancon Construction Ltd, CONTENUR coordinated installation during key landscaping phases of the project. This approach ensured seamless integration with surrounding works while maintaining the highest standards of safety and heritage sensitivity.
Since the castle’s reopening in December, the completed installation has delivered multiple operational benefits. Waste is securely stored underground, improving hygiene standards, reducing odours and supporting a safe and efficient collection process. At the same time, the castle grounds remain visually uncluttered, allowing visitors to fully appreciate the historic setting.
As Inverness Castle embarks on its next chapter as a major visitor destination, CONTENUR’s underground waste solutions are already contributing to the site’s long-term sustainability and overall visitor experience. The project demonstrates how modern infrastructure can successfully support historic environments without compromise.
RCP | Rubbermaid Commercial Products launches new range of stylish yet functional solutions for small spaces
Rubbermaid Commercial Products (RCP) has today announced the expansion of its waste and recycling range with stylish solutions designed for light traffic areas under their “Rubbermaid” brand.
Combining elegant aesthetics with practical performance, the five new bins help to make waste management effortless, even in areas where space is limited. Ideal for boardrooms, receptions, washrooms and front-of-house – the new products feature dual-stream capacity to help boost recycling rates in locations where efficiency, style and sustainability are key priorities.
Designed to impress, built to perform
Changing demands are driving modern facilities to explore new solutions for effective waste management. There’s a growing need for aesthetically pleasing products that blend into interiors. At the same time, legislative pressure and changing regulations mean that customers are looking to products that can ensure recycling takes place in every part of their facilities, including areas where it would not have been previously possible.
Available to order now, RCP’s waste and recycling range features five new designs that meet these needs, bringing function and elevated aesthetics to any facility:
Rubbermaid 6L Stainless Steel Round Pedal Bin Wastebasket, Charcoal – Compact and low-maintenance, this bin is ideal for professional washroom and hospitality environments. It features a slow-close lid, hands-free pedal, removable liner and bag cinch system, in a charcoal stainless-steel finish that hides fingerprints, smudges, and dirt.
Rubbermaid Elite 45L Stainless Steel Pedal Bin – Sleek and modern, the Rubbermaid Elite 45L features a low-maintenance finish that hides fingerprints. With hands-free operation and a slow-close lid, it’s ideal for hotels, offices, and front-of-house spaces.
45L Stainless Steel Pedal Bin – Sleek and modern, the Rubbermaid Elite 45L features a low-maintenance finish that hides fingerprints. With hands-free operation and a slow-close lid, it’s ideal for hotels, offices, and front-of-house spaces.
Rubbermaid Elite 60L Stainless Steel Pedal Bin, Dual Stream – Streamlined and efficient, the Rubbermaid Elite 60L Dual Stream features colour-coded liners for easy waste separation. With hands-free operation, a quiet-close lid, and fingerprint-resistant finish, it’s ideal for workplaces, hotels, and office facilities.
60L Stainless Steel Pedal Bin, Dual Stream – Streamlined and efficient, the Rubbermaid Elite 60L Dual Stream features colour-coded liners for easy waste separation. With hands-free operation, a quiet-close lid, and fingerprint-resistant finish, it’s ideal for workplaces, hotels, and office facilities.
Rubbermaid Premier® Series II 46L Pedal Bin, Charcoal – Built for performance and designed to fit with modern facilities, this bin is ideal for small offices and hospitality environments.
Rubbermaid Premier® Series 71L Pedal Bin, Charcoal, Single or Dual Stream – The perfect marriage of form and function, this large-capacity bin features a stainless-steel foot pedal, integrated LinerLock, and interior venting to make removing rubbish bags simple.
Waste management, reimagined
The new products in the waste and recycling range are welcome additions at a time when facilities are under increasing pressure to improve recycling rates in order to cut costs and deliver on sustainability.
“We’re thrilled to unveil our expanded range of stylish yet functional Waste & Recycling solutions,” said Emilio Capelli, VP Sales & Marketing, RCP EMEA.
“We have always strived to develop solution-based products that support the hard workers who keep the world working. Right now, those workers need solutions that help them deliver on waste management and recycling in every area of their operations. But they also need stylish solutions designed to fit in seamlessly into environments, keeping bins on brand with their facility. That’s why we have expanded our range so that light-traffic areas can benefit from the same waste management systems as every other area of your facility.”
For more information about the RCP waste and recycling range visit: www.rubbermaid.eu/en/rubbermaid-range/.
CRJ Services | Specialist NPORS Training for Waste, Recycling & Forestry Machinery
CRJ Services is proud to offer NPORS-accredited operator training and CSCS card pathways, designed specifically for operators working in waste processing, recycling, forestry, and industrial plant operations.
With over 25 years of hands-on industry experience, CRJ delivers practical, machine-focused training that helps operators work safer, more efficiently, and in full compliance with UK site requirements.
Whether hiring or purchasing equipment, we ensure our customers receive the right training from day one. This gives you peace of mind that your operators know exactly what to check, how to work safely, and how to spot potential issues early. The result? Better cost per tonne and less downtime through increased operator awareness.
Expert OEM Machine Training
With 11 years of on-the-job, OEM-trained experience, Joe Symons is CRJ Services’ in-house trainer. Recently qualified as an NPORS Instructor, Joe delivers internal and external training grounded in real-world site conditions, with a strong focus on safe working practices, legal compliance, and efficient machine operation. His practical, experience-led methods ensure all trainees understand not just how to use equipment, but why following the right procedures is so important in the challenging world of forestry, recycling, and waste management.
CRJ Services is uniquely positioned to deliver specialised OEM operator training, led by in-depth knowledge and experience of the forestry, waste and recycling service industries.
Available courses provided by CRJ:
- N208 Screener
- N603 Wood Chipper- Shredder
- N209 Loading Shovel
- N202 Excavator 360°
- N120 Plant Loader Securer
- N010 Telescopic Handler
- N001 Industrial Counterbalanced Lift Truck
- N722 Material Re-Handler
- N106 Log Handler With special focus on:
- Safe machine operation
- Site safety and risk awareness
- Load handling and material flow
- Pre-use checks and maintenance awareness
- Emergency procedures
- Maximising machine efficiency
- Reducing downtime and costly operator errors
This ensures operators don’t just pass an assessment, they understand how to get the best performance from the equipment while operating safely.
Whether you’re looking to upskill existing operators, meet site compliance requirements, or invest in accredited training for new starters, CRJ Services can support your business.
Simply fill in our form (insert link: https://crjservices.co.uk/training/) or contact Joe at training@crjservices.co.uk to discuss further.
Vision Techniques | Vision Techniques revamp best-selling product reflecting the changing needs of modern fleets
Commercial vehicle safety and security specialists, Vision Techniques, have given one of their products a revamp.
The VT Ident Plus System, one of the company’s best-selling products, has been given a major upgrade, offering even more benefits to customers.
The system is designed to prevent thefts, accidents and unauthorised vehicle use by ensuring only trained and authorised operators can start and operate vehicles and/or equipment, with built in anti-rollaway protection.
The intelligent driver and vehicle authorisation system already came with a variety of benefits including improved operational efficiency, fuel savings and complete controlled access.
However the new system has been upgraded to now offer even more benefits. These include flexible authentication options including passive RFID tags, cards, pin codes as well as integrated telematics for live vehicle tracking via VT Connect.
This means the product can now track driver activity and behaviour, as well as full visibility of driver usage, access attempts and events.
As well as benefitting from all the product upgrades, customers will also get the first year data subscription included in the cost of the system.
Mikaeel Koornhof, Technical Specialist at Vision Techniques, shares what inspired the upgrade.
He said: “The latest evolution of VT Ident Plus reflects the changing needs of modern fleets.”
“Customers are looking for more than access control, they want visibility, accountability, and data they can act on.”
“By integrating telematics, expanded authentication methods, and VT Connect reporting, we’ve enhanced safety, reduced risk, and given fleet operators greater control over how their vehicles are used.”
“The system now supports multiple driver authentication options, detailed driver and vehicle activity logging, live tracking, and configurable vehicle-specific authorisation, while built-in failsafe’s such as park brake monitoring further strengthen on-site and road safety.”
Vision Techniques are the innovative driving force in vehicle safety and security systems, protecting not only vehicles but also the lives of employees, the public and the environments they operate in.
Chosen by some of the largest fleets in the UK, Vision Techniques’ products are influencing and changing safety and security standards across industries daily.
To find out more about Vision Techniques go to: www.vision-techniques.com.
Dennis Eagle | Dennis Eagle and Terberg Matec UK’s Sales and Aftermarket teams have integrated
Market leader for refuse collection vehicles in the UK, Dennis Eagle recently announced plans to combine its Sales and Aftermarket teams with those of its subsidiary division, Terberg Matec UK.
The integration of these teams will see customers benefit from one unified service, offering a single point of contact for any sales and aftersales enquiries respectively. By aligning its resources and industry-leading knowledge, Dennis Eagle intends to deliver more rapid, reliable, and streamlined support to its customers.
“This transformation marks a pivotal moment in our evolution,” said Keith Day, Managing Director, Dennis Eagle. “By bringing these highly experienced teams and their technical expertise together, we are better enabled to deliver exceptional engineering, service excellence, and long-lasting value to our customers. As we move forward, we remain united in our purpose to exceed expectations and provide an outstanding service at every stage of the customer journey.”
As a result of the integration, the sales of all refuse chassis, bodies, bin lifts, and dynamic weighing solutions will now be managed from Dennis Eagle’s Warwick facility, with chassis manufacturing continuing at Blackpool, and Northwest Field Service activity and OEM operations now managed from Warrington. The sales and manufacture of any specialist recycling vehicles will remain within the Worksop facility. To provide the best possible customer experience, all technical experts will be cross trained on both Dennis Eagle and Terberg Matec UK product portfolios, supported by the business’ new Technical Training Centre.
“The integration of our Aftermarket teams is an exciting step towards a better future for both our business and our customers,” said Geoff Rigg, Aftermarket Director, Dennis Eagle. “As customer expectations shift, we want to keep ahead of the curve and harness our combined experience to proactively address new industry challenges as they emerge. Through this unified, consistent approach, we’re able to provide the same world-class service our customers expect across the entirety of our product portfolio.”
The integration came into effect from 5 January 2026.
The post News in brief | CIWM Commercial Partner Updates 30 January appeared first on Circular Online.